The ignition coil is equivalent to an autotransformer which can convert 12V low-voltage direct current into 15-20KV high-voltage direct current.
According to the structure of the magnetic circuit, the ignition coil can be divided into two types: open magnetic circuit type and closed magnetic circuit type.
Open magnetic circuit ignition coils are widely used in traditional ignition systems。
Closed magnetic circuit ignition coils are mostly used in electronic ignition systems.
Structure of ignition coil:
1. Shell
2. High voltage terminal
3. Low voltage terminal
4. Insulating oil
5. Primary winding
6. Iron core
7. Secondary winding
8. Additional electric just
Primary winding: The primary winding is wound 240 to 370 turns on insulating paper with enameled wire with a diameter of 0.5 to 1.0 mm. In order to facilitate heat dissipation, the primary winding is wound outside the secondary winding, and the primary winding resistance is about 3.4 omega (80 degrees Celsius).
The secondary winding uses enameled wires with a wire diameter of 0.06 to 0.10 mm wound around the outside of the core insulating sleeve, about 11,000 to 26,000 turns. In order to strengthen the insulation and avoid mechanical damage, each layer of wires is separated by insulating paper. The outermost layer There are more layers of insulating paper, or a cardboard sleeve is covered. Its function is to generate mutual inductive electromotive force.
Let’s take a look at the teardown diagram:
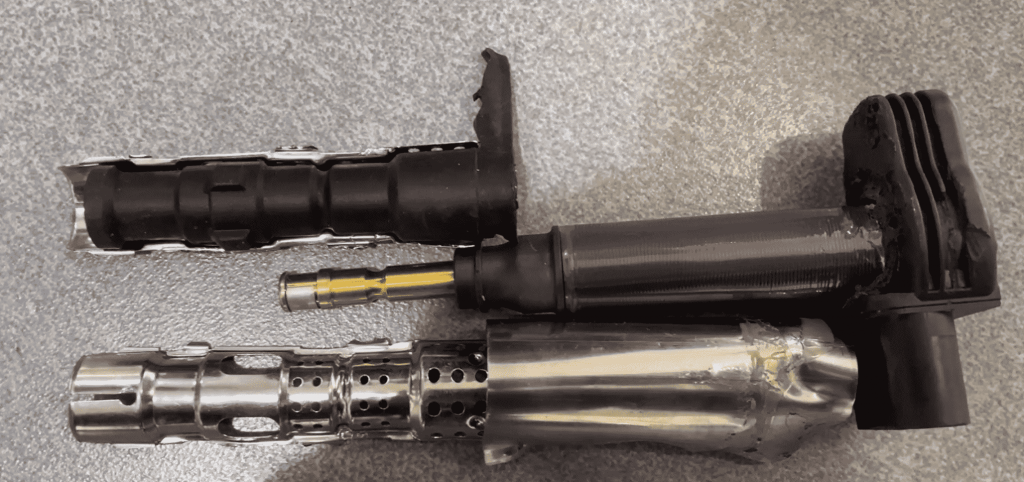


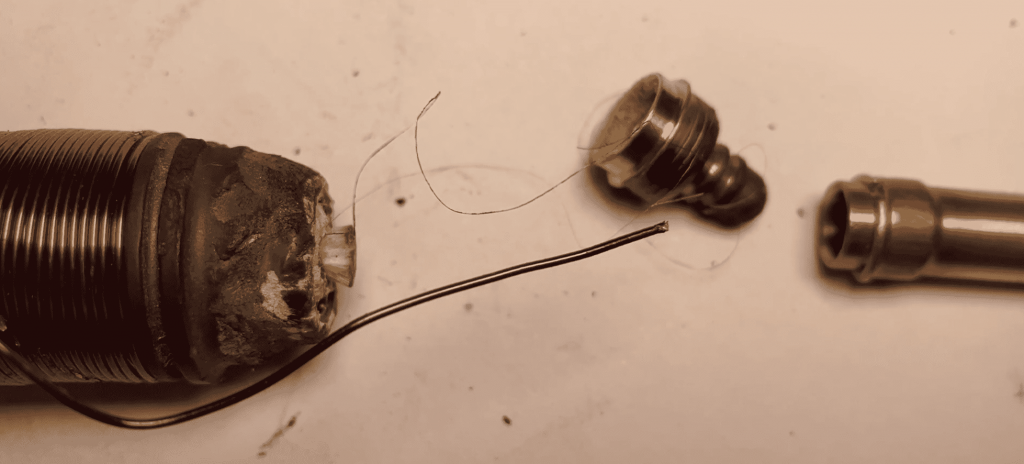
Ignition Coil Failure Phenomenon and Practical Inspection Methods
How To Remove And Install The Ignition Coil By Yourself?
Simple And Practical Ignition Coil Detection Method
How To Produce Ignition Coils?
How Ignition Coils Work
Do We Have To Use The Original Ignition Coil?

